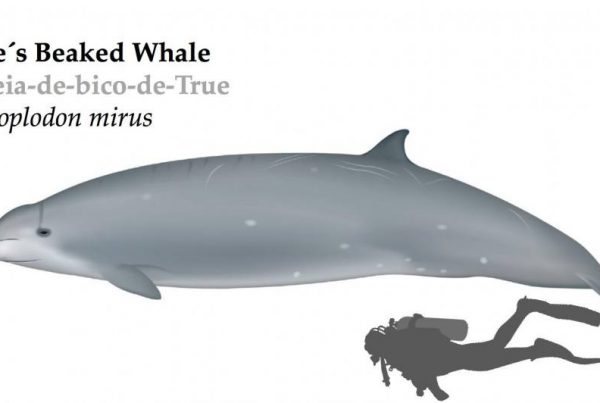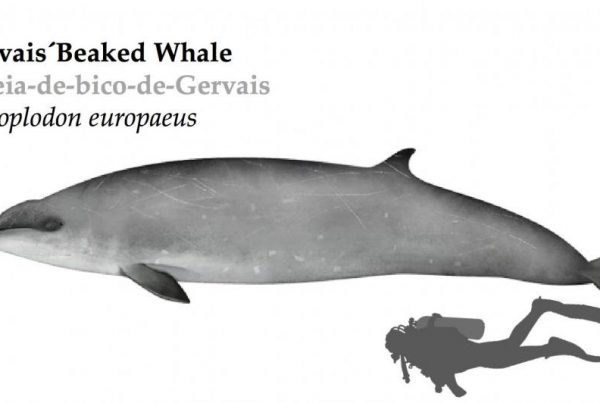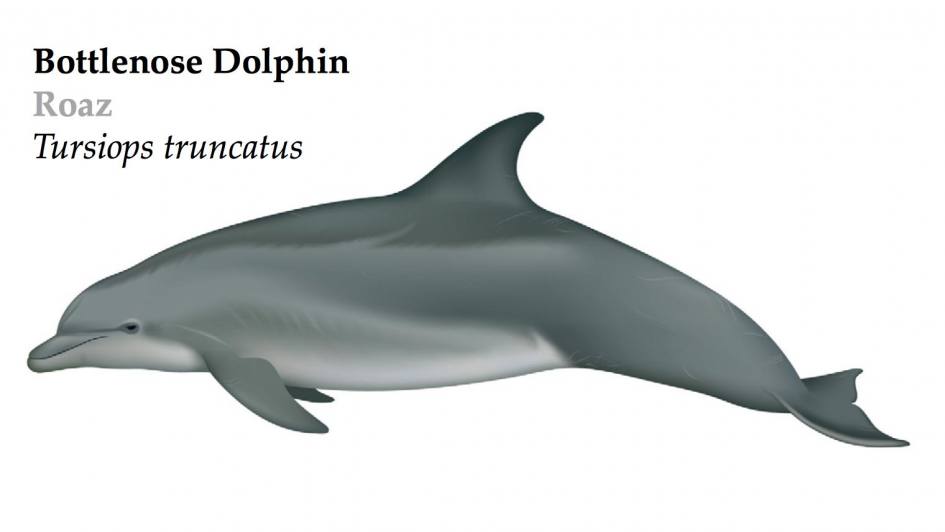
The Bottlenose dolphin is the most recognizable and iconic dolphin species. They have been portrayed in TV shows and movies (e.g., Flipper). Like the name « bottlenose » suggests, bottlenose dolphins have a short stubby beak.
CHARACTERISTICS
- Latin name : Tursiops truncatus
- Suborder : Odontoceti
- Family: Delphinidae
- Length : 2 to 4 m
- Weight : 150 to 650 kg
- Dive time : up to 15 minutes
- Dive depth: 300 m
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
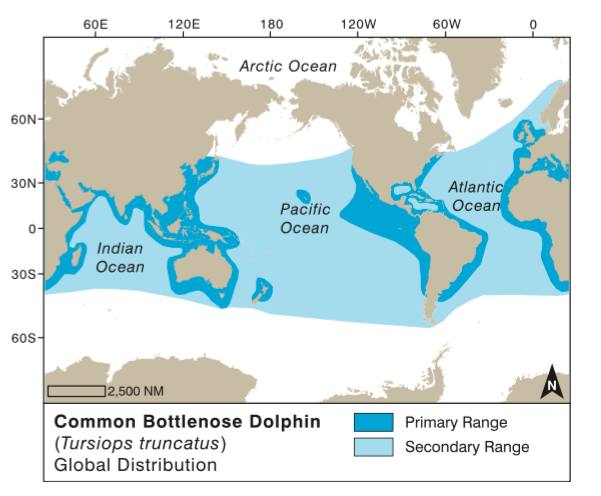
Worldwide distribution of Bottlenose dolphin. Source: Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals IIIrd Ed. Bernd Würsig, I. G. M. Thewissen & KIT M. Kovacs
DESCRIPTION
Color: The back is dark grey and the belly is lighter.
Head: Pronounced furrow between the melon on top of the head and the beak.
Fins: Dorsal fin in the center of the back, sickle shaped.
Teeth: 40 to 50 conical teeth in the upper jaw and 30 to 50 in the lower jaw.
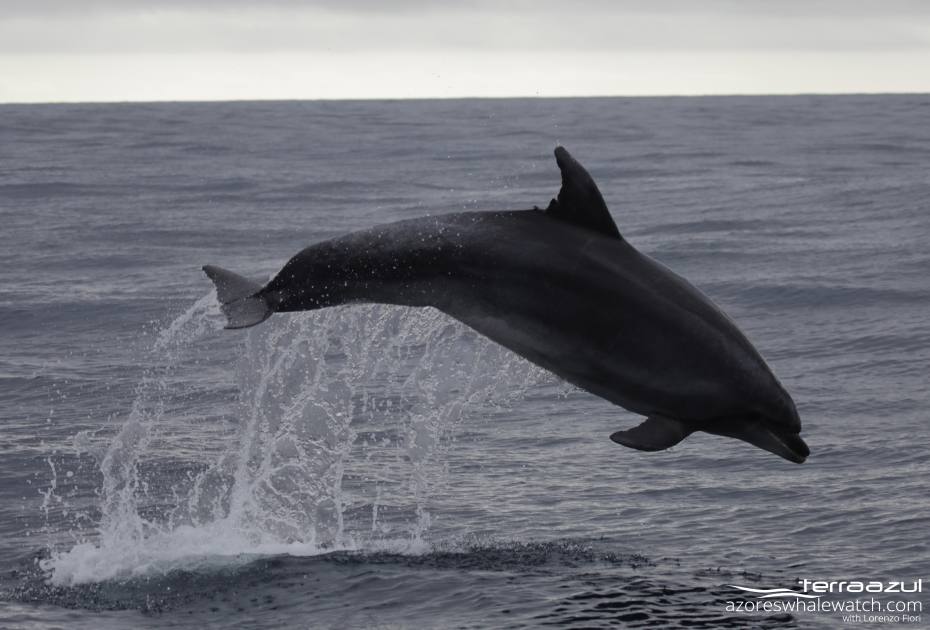

Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) leaping out of the water.
LIFE HISTORY
DIET
Schooling fish (e.g., herring, anchovies, sardines, mackerels), squids and even small crustaceans. In some regions bottlenose dolphins learned to feed on octopus, stunning the prey on the water surface before to swallow it. Bottlenose dolphins use different cooperative feeding strategies depending on the environnement where they live. In some places of the word, they feed trapping the fish in a circle of mud lifted from the sea floor by vigorous tail slaps. In other regions, bottlenose dolphins have been observed voluntarily stranding themselves to capture fish in shallow waters. In some coral reefs, bottlenose dolphins attach sponges to protect their beaks while they hunt preys hidden in the corals. Finally, some bottlenose dolphins populations in Central Africa and Brazil have learned to cooperate with fishermen scaring the fish towards the shore where the nets are deployed and getting a reward from the fishermen afterward.
REPRODUCTION
Breeding take place in the spring and the gestation is around 12 months. At birth, the calf size is around 90-120 cm. Nursing lasts 12 to 15 months even though the calf starts eating solid food well before that.
SOCIAL BEHAVIOR
The bottlenose dolphin is a gregarious marine mammal. They live in family pods ranging from a few to hundreds of individuals. Once males reach sexual maturity, they tend to leave the family pod and form bachelor groups of individuals with similar age. Males are also reported to form strong alliances that can even last for all their lives. Two ecotypes of bottlenose dolphins are recognized: coastal and offshore. Coastal bottlenose dolphins are generally smaller and paler than the offshore ecotype. While the two ecotypes seem not to mix, offshore bottlenose dolphins can form large multi-species aggregations with pilot whales and false killer whales.
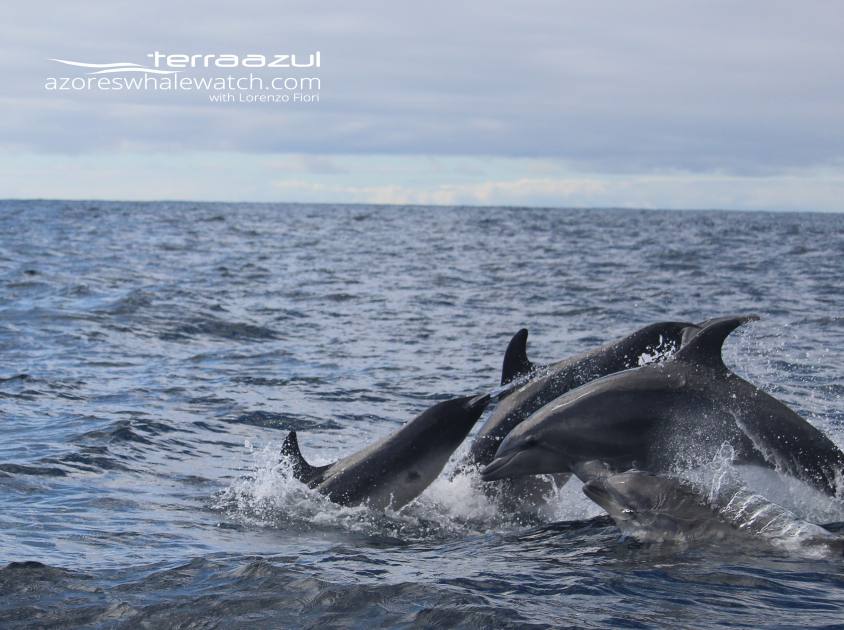

A pod of Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) porpoising.
VOCAL BEHAVIOR
Bottlenose dolphins produce several different sounds and ultrasounds used in social interactions and in echolocation to detect the prey. They emit whistles, groans, squeaks and series of ultrasonics clicks called harmonics. Each individual can emit a signature whistle which is unique to that particular individual. It has been documented that other dolphins can mimic the signature whistle of another individual when they want to communicate with it. You can listen bottlenose dolphins communicating in this recording collected by Terra Azul Crew.
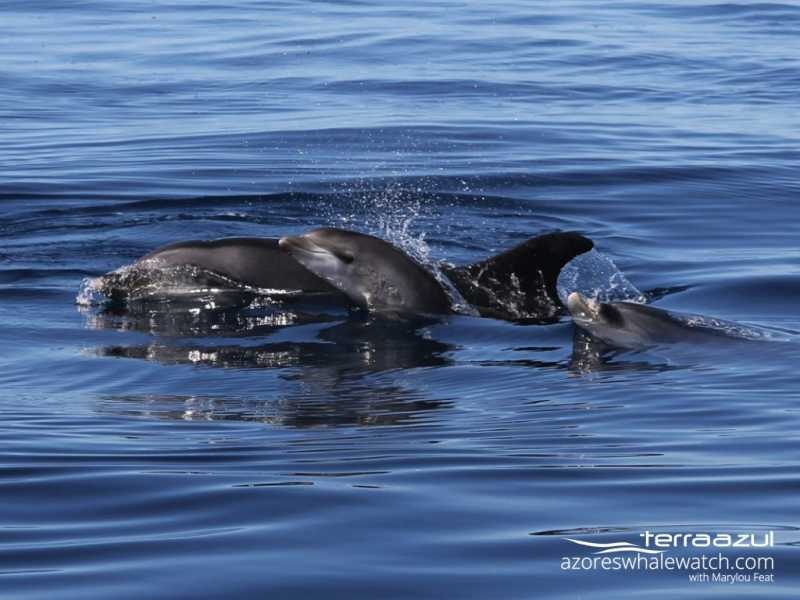

A calf of Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) travelling next to its mother.